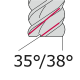
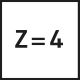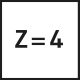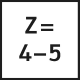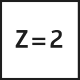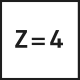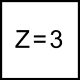Skaftfräsar
I vår webbutik hittar du ett omfattande sortiment av högkvalitativa Walter Tools skaftfräsar. På produktsidan kan du se skaftfräsarnas exakta mått, kontrollera produktens lagerstatus, prisinformation samt ladda ner en 3D-modell av skaftfräsen för import till CAM-programvara. Skaftfräsar är en verktygstyp som används för fräsning av små former, såsom fickor, urtag, spår och olika typer av spår, inklusive kilspår. Skaftfräsar tillverkas vanligtvis av antingen snabbstål eller hårdmetall. Hårdmetallfräsar är numera vanligast tack vare sin höga kvalitet och produktivitet. Det finns olika typer av skaftfräsar för olika användningsområden, såsom hörnradiefräsar, fräsar utan hörnradie, radiefräsar samt dynamiska fräsar.
Läs meraSkaftfräsar
End mills are the most common tool type for milling small shapes. End mills are primarily made of high-speed steel or carbide. The quantity of high-speed steel end mills has been steadily decreasing in recent years, and they are now mainly used on manual milling machines.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is a hard-grade steel known for its good toughness and wear resistance, making it suitable for manufacturing cutting tools. Although high-speed steel tools are no longer the most efficient tools in the machining industry, they still have their place in unstable conditions, for single-piece production, and manual mills.
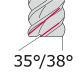
Solid carbide end mills are valued for their quality and cost-effectiveness in relation to tool productivity and the machining processes enabled by modern machines, making them the most common end mill model. Carbide is a metal matrix composite characterized by excellent wear resistance and toughness, where tungsten carbide (WC) particles are bound in a cobalt (Co)-rich binder. Generally, all carbide tools are coated with different finishes. In the machining of high-temperature superalloys and titanium alloys, uncoated carbide tools can also be used.
There is a wide variety of end mills for different applications, such as traditional straight end mills for corner and slot milling, long-cutting edge end mills with multiple cutting edges for dynamic milling, and end mills with large-end radii for high-feed milling, as well as ball or barrel end mills for milling 3D surfaces and various rounding, chamfering, T-slot, and dove-tail slot end mills.
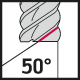
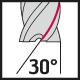
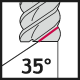
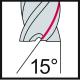
The most common type of end mill is the straight end mill, which is suitable for both roughing and finishing milling across a wide range of material groups. End mills can have either a straight cylindrical shank or be equipped with Weldon flats. The corners of the cutting edges on straight end mills can be sharp or rounded/chamfered. Most commonly, straight end mills have 2-4 cutting edges, but when working with soft materials like plastics, single-edge tools are used, and for finishing, tightly spaced edge mills with 6-8 cutting edges are used.
A straight end mill can also be a dynamic end mill, designed for the modern toolpaths generated by CAM software. Dynamic end mills feature a long cutting edge (3-5xD) and multiple cutting edges (5-8). The chip flutes on dynamic end mills are shallower than in traditional end mills, resulting in a larger core that ensures tool stability even with deep cuts. Most dynamic end mills come with chip splitters that break the chips into short pieces.
Radius end mills, commonly referred to as "ball end mills," are popular for machining 3D surfaces. A radius end mill is similar to a straight end mill but has a rounded nose. The rounded tip allows for milling a variety of 3D surfaces commonly required in mold making. Modern 5-axis machines allow the use of barrel end mills, similar in principle to ball milling but with large radii machined into the sides. The large radius makes barrel end mills more effective than traditional ball end mills.
High-feed end mills employ a large edge radius at the tool's tip. The tool runs at shallow depths but with high feed rates. Due to the high feed rate, high-feed end mills are excellent for roughing small grooves and pockets.
Chamfer and rounding end mills are designed explicitly for chamfering and rounding edges of parts, as their names suggest.