Geometric Tolerances Run-out Cirlucar Run-out
Run-out (in English, "run-out") is a tolerance that defines how much the actual shape and position of a rotating feature may deviate from the ideal rotary motion. Run-out controls both form and position errors when the part is evaluated during rotation relative to a datum. It is especially important in rotating parts where even a small inaccuracy can cause imbalance, vibration, or excessive wear.
Run-out is one of the basic geometric tolerances defined in the ISO 1101 standard and serves as a kind of “composite tolerance,” as it includes various form and positional accuracy factors together.
Applications
- Shafts and bearing surfaces: ensures the shaft rotates smoothly without excessive wobble.
- Holes and sleeves: prevents irregular rotation that could lead to joint loosening or wear.
- Rotating components: such as brake discs, gears, and crankshafts, where even a small run-out can have a significant impact on function.
Notation and interpretation
The measured (actual) line must, in every plane perpendicular to the common datum axis A–B, lie between two concentric circles in the same plane whose radius difference is 0.1.
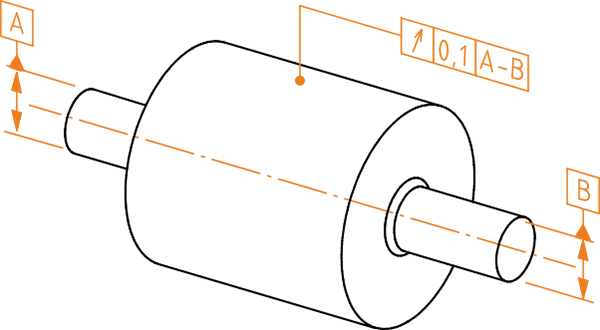
Definition of the tolerance zone
The tolerance zone is limited, in every cross-sectional plane perpendicular to the datum axis, by two concentric circles whose radius difference is t and whose centers lie on the datum axis.
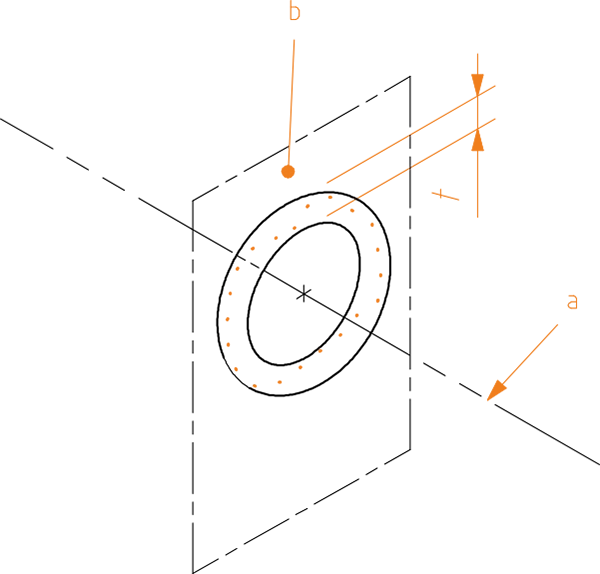
Importance in manufacturing
Run-out is a critical tolerance because it directly affects the functionality and service life of a part. Excessive run-out often leads to noise, vibration, seal leaks, and accelerated wear. For this reason, it is commonly used, especially in machine parts that rotate or need to be precisely aligned around an axis.
It should also be kept in mind that measuring and controlling run-out requires special tools, such as dial indicators or coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). Overly tight requirements increase costs, so the tolerance should only be as precise as necessary for the functionality.
Run-out tolerance according to ISO 1101 provides a clear and internationally consistent way to ensure that rotating parts operate smoothly and reliably.

